Recent stats say that more than 65% of manufacturers still leverage some forms of manual inspection on site, which results in frequent product recalls, and what’s worse, potential damage to business reputation. Besides, even if advanced techs are used, 20% of defects tend to go unnoticed to the market, making companies lose a staggering $1.3 trillion annually.
Fortunately, a newly introduced computer vision anomaly detection steps in to solve the issue. What visual inspection in manufacturing is, what’s under the hood, how such automation can revamp your manufacturing business, read on to solve the puzzles.
How computer vision defect detection works in manufacturing
AI visual inspection solutions leverage the power of cameras, sensors, advanced ML algorithms, and powerful BI reporting to prevent defective items from entering the market. Here’s how the pipeline looks like.
Stage 1: Image acquisition
The first stage includes obtaining high-quality images of the very equipment and items on the line. This is done through high-resolution industrial 2D and 3D cameras with the control of lighting. LED ring or dome lights are usually used to eliminate shadows and highlight even subtle flaws.
Stage 2: Pre-processing
At this phase, raw images are filtered and augmented through specific refinements, including:
- Noise reduction. Leveraging techniques like Gabor filters or wavelets to smooth the image, eliminate sensor interference, and emphasize defect-specific textures.
- Normalization: changing brightness, contrast, color, and saturation for better environmental consistency.
- Geometric correction: eliminating distortions caused by camera lens, incorrect angles and positions, and camera movements to align the image with a real-world coordinate system.
Stage 3: Feature extraction
This stage presupposes that key attributes (edges, landmarks, textures, shapes, colors, and patterns) are identified to convert massive raw datasets into a strictly defined set of characteristics. Convolutional Neural Networks automatically learn these features to spot “good” or “defective” parts for future analysis.
Stage 4: Analysis
During the analysis stage, the extracted features are examined to spot anomalies or defects in items or equipment. In other words, they’re analyzed against the reference model / normal behavior to find deviations. For example, when inspecting metal bolts, the system analyzed its length, diameter, and surface smoothness. And if the length exceeds 50 mm or surface roughness is high (there’re scratches) the bolt is automatically flagged as defective.
Stage 5: Decision-making
The classification of images / regions like normal or defective can be performed based on labeled training data (SVM, Random Forest, etc.) or through unsupervised learning techniques (clustering, PCA, autoencoders). Anomalies should also be scored here based on type, the degree of deviation, whether an image or region is anomalous, whether deviations are persistent or transient, etc.
After the anomaly is classified, production actions are triggered. This might include automatically rejecting defective items in the production line, notifying operators via dashboards, recording results for traceability, or asking for human judgment in ambiguous cases.
All the results are recorded in manufacturing execution systems (MES) for seamless operation. The visual inspection manufacturing solution also implies sophisticated learning mechanisms so that the algorithms could be continuously refined and adjusted based on context.

Capitalize on AI visual inspection
in manufacturing
Vision AI for visual anomaly detection: Major benefits
Implementing visual anomaly detection in manufacturing might seem costly at the beginning, but it’ll give your more bang for your buck. Here’s tangible value you’ll get for your manufacturing business.
- Enhanced efficiency. Automated computer vision systems outperform manual inspection, achieving near-zero error rates. Microscopic flows (micro-cracks, texture deviations, sub-millimeter surface defects) are detected in seconds 24/7, without any fatigue or bias, thus increasing overall throughput at least by 30%–52%.
- Cost savings. By automating manufacturing defect detection, you can not only slash direct costs in labor and error, but only reduce waste costs (raw materials, energy, etc.), i.e. costs that are spent on re-producing faulty parts. As a result, you can notably decrease scrap rates, lower the risk of costly item recalls, and minimize downtime.
- Workplace safety and compliance. Visual inspection in manufacturing presupposes identifying safety hazards at the workplace, including spills, leaks, abnormal behaviors, overheating, obstructions, or misplaced objects, thus preventing accidents. Worker protection is also guaranteed through safety gear monitoring (helmets, gloves, vests, etc.).
- Traceability and compliance. By thoroughly checking correct assembly, labeling, and safety features, computer vision systems ensure products and processes comply with the highest industry regulations. Depending on your niche, it might be FDA, OSHA, or ISO standards. Moreover, detailed reports about inspections (with images and metadata) are automatically logged for transparency and traceability.
Leverage our ChatGPT development services to build a visual inspection solution.
Visual inspection in manufacturing: Key use cases
Computer vision perfectly finds its feet in an array of real-work situations in manufacturing settings, and its advanced implementation will bring substantial value to your business.
Advanced quality assurance
As we’ve mentioned earlier, computer vision defect detection is one of the primary functions of AI visual inspection solutions. Here’re the details about how you can benefit from this tech.
- Manufacturing defect detection. Computer vision-fueled systems are able to automatically identify defects that are invisible to the human eye, with high precision. This might include hairline cracks (fractures, fissures), edge chips, micro-tears in textiles, and pinholes in products, electronics, automotive parts, or packaged goods. They’re then classified based on severity and type, ensuring rapid rejection of faulty items.
- Assembly verification. AI visual inspection solutions check that all components of your item are present, correctly assembled, oriented, and placed. The examples include identifying insufficient or excessive solder, bridges, and icicles (that cause field failures), detecting missing chips or misaligned connectors, or checking the orientation of tiny components on high-density circuit boards (resistors, capacitors, connectors).
- Surface quality inspection comprises verifying surface uniformity, color consistency, and finish quality. Any surface blemishes (minor scratches, scuffs, or uneven spots), process irregularities (glue spills, paint bubbles, welding splatter), cosmetic flaws (discoloration, stains, wrinkles), and contaminants (foreign particles, dust, fibers, oil / water spots) are detected automatically.
Machinery predictive maintenance
Computer vision is able to continuously monitor asset health, preventing failures and as a result costly downtime.
- Thermal anomaly detection. The infrared and thermal cameras installed in manufacturing settings are able to spot abnormal heating in motors, electrical cabinets, or furnaces, this way, alerting potential overheating or friction a way before the actual breakdown or a fire occurs.
- Dynamic wear analysis presupposes calculating the Remaining Useful Life (RUL) of machinery parts through the comparison of real-time images against the optimal baseline states. In turn, part replacement is performed exactly when needed, preventing unplanned stoppages.
- Leak identification. To avoid equipment damage and safety hazards, vision AI continuously monitors the environment and identifies seal failures, i.e. escaping fluids, gas, or steam, as well as build-ups of dirt and debris in pipes and filters.
Worker safety
On top of technical use cases around equipment monitoring, vision AI for visual anomaly detection brings its fruits in the context of human safety.
- Danger zone monitoring. Cameras installed in hazardous zones feed live video streams into AI systems trained to recognize humans and machinery. Then, proximity analysis is performed to calculate the distance between workers and the dangerous area. If unsafe behaviors that break safety protocols are detected, the system sends alerts and, if needed, communicates with the machinery to temporarily shut down the operations.
- Rule compliance monitoring. By easily and instantly detecting Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) like hard hats, helmets, high-visibility vests, safety glasses, gloves, face shields, and respirators, computer vision systems spot non-compliance and prevent possible incidents.
- Worker fatigue detection. With advanced behavioral monitoring, AL algorithms can not only track worker adherence to specific safety protocols (lockout/tagout procedures, designated walkways, safe distances from moving vehicles, etc.), but also identify specific physical signs of exhaustion. The latter includes analyzing eye dynamics (prolonged blinks, drooping eyelids), face expressions (yawning frequency and intensity), head movements (sudden jerks, nodding,), and ergonomic micro-compensations (slower arm responses).
Logistics and inventory management
Computer vision capabilities go beyond item defect detection and comprise aspects like packing, labeling, and logistics.
- Inventory monitoring. Ceiling-mounted cameras and autonomous drones navigate aisles to scan barcodes, QR codes, and labels, helping human workers update warehouse management systems in the blink of an eye. With such automated continuous oversight, phantom, misplaced, and low-stock items are also discovered.
- Automated sorting and packing. Underpinned by trailblazing mechanisms, computer vision solutions perform automated load verification, making sure the products meet shipping manifests, as well as have proper quantities and delivery sequences. AI-fueled robots not only automatically sort, pack, and place items, but also calculate the most efficient stacking patterns, while boosting trailer capacity and cutting down shipping costs.
- Logistics optimization. AI visual inspection solutions perform advanced vehicle monitoring, analyze forklift routes, and identify traffic patterns to create so-called heatmaps, optimize warehouse layouts, minimize congestion, and prevent collisions. Real-time tracking of dock activity is also performed (including the analysis of estimated cycle times for appointments and photographic proof of pickup), helping manufacturers reduce insurance claims. Besides, the system alerts when drivers enter restricted areas and safety protocols (like wearing PPE) are violated.
Team up with Aetsoft for deploying visual inspection in manufacturing
Once you’ve decided you need visual inspection automation to reinforce your manufacturing processes, Aetsoft is here to assist. Our seasoned experts in artificial intelligence and machine learning created a custom AI platform for cognitive vision to accelerate the implementation of manufacturing defect detection in your settings.
You don’t need to build costly solutions and hardware from scratch, our platform boasts a modular and hardware-agnostic architecture, which presupposes smooth pairing up with existing cameras, systems, and sensors.
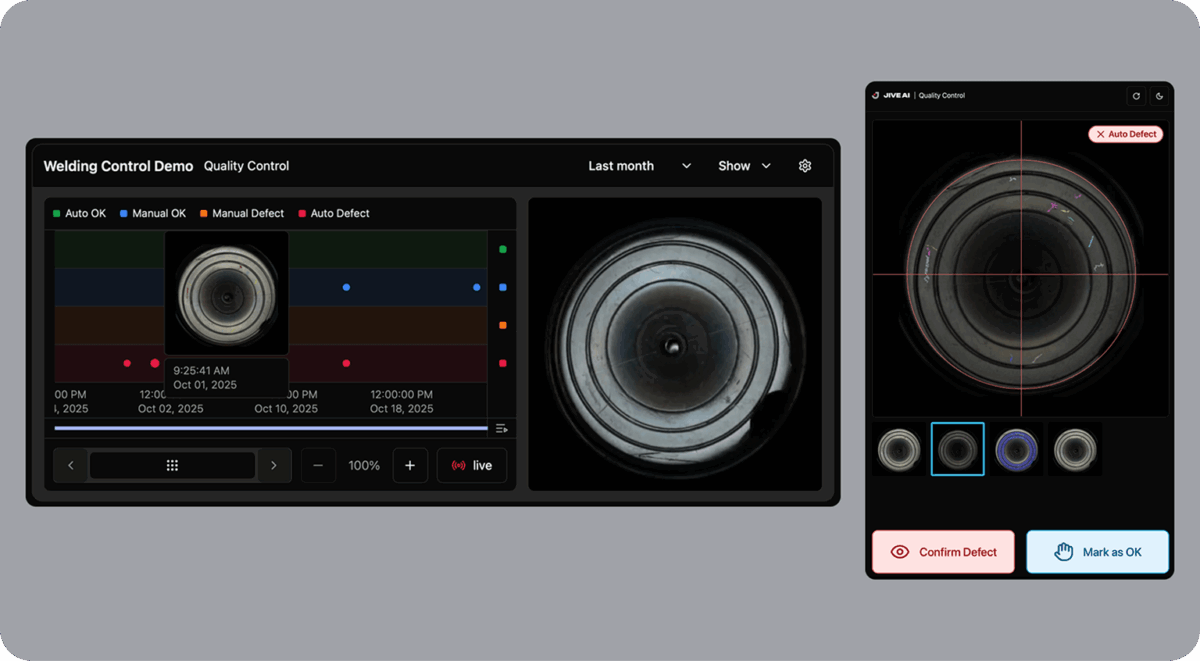
We created a platform that can constantly filter visual noise to spot relevant anomalies and understand the context while prioritizing meaningful events. This helps drive tangible insights (in the form of easy-to-trace centralized dashboards) and act before small issues turn into incidents.
Our cognitive vision solution offers human-centric UI, consistent performance regardless of deployment size, rock-solid cybersecurity out of the box, and the offline mode in regulated facilities. Powerful industrial integrations, OPC-UA / REST / MQTT connectivity, edge / cloud / hybrid setups, IP67 compliance — you’ve got your back.
Our proprietary solution can be easily customized to your particular industry and specific vision needs. You can connect with us right now to discuss the details.
FAQ
What is AI-based visual inspection in manufacturing?
Automated visual inspection in manufacturing settings represents a fusion of techs and hardware, namely, industrial cameras (with specialized lighting), sensors, and artificial intelligence to automatically analyze items for defects, assembly errors, and inconsistencies.
Why is AI-fueled visual inspection important for manufacturing?
Unlike in traditional reviews, where human workers inspect all the equipment manually, computer vision-driven platforms detect subtle anomalies much more rapidly and accurately. This results in benefits like enhanced efficiencies, slashed costs, and increased security.
What tools and techniques are used in automated visual inspection?
Specialized visual inspection platforms leverage computer vision algorithms, machine learning models, and convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to analyze images and video for defect detection. Among specific image processing techniques is object recognition, edge detection, texture analysis, pattern recognition, optical character recognition (OCR), face recognition, behavior analysis, and more.
How does automated visual inspection in manufacturing improve quality?
Automated systems are able to detect microscopic flows and sub-millimeter surface defects that are usually missed by a human eye. Moreover, this is done in milliseconds and around the clock, leading to increased overall efficiency and quality standards compliance.






